APIs are the backbone of modern apps. But when they slow down, everything from your user interface to your entire business logic starts lagging.
You’ve built a great API, but users still complain that your app is slow. It’s not always your frontend your API might be the hidden bottleneck.
In this post, we’ll go step-by-step through the most effective ways to optimize API performance without trying ourselves to any specific framework. Think of this as your checklist for building lightning-fast, scalable APIs.
1. Optimize Data Flow and Payloads
Key Idea: Send only what’s necessary. Smaller payloads = faster responses.
Examples to mention:
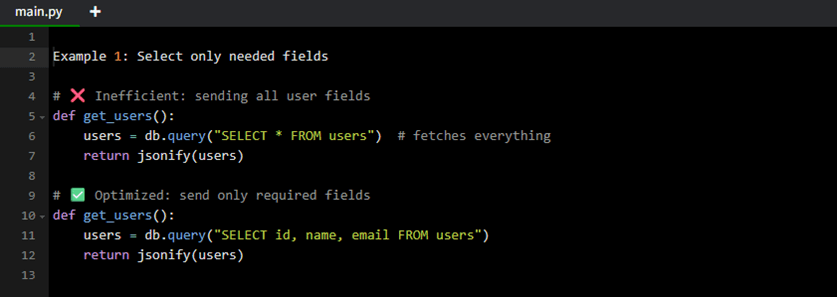
- Avoid sending entire objects when you only need a few fields.
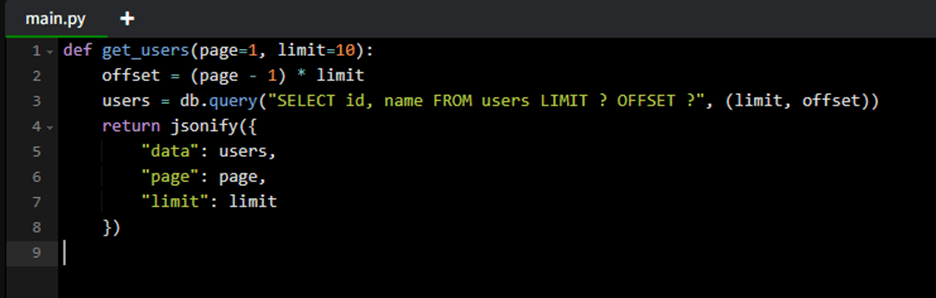
- Use pagination for large datasets.
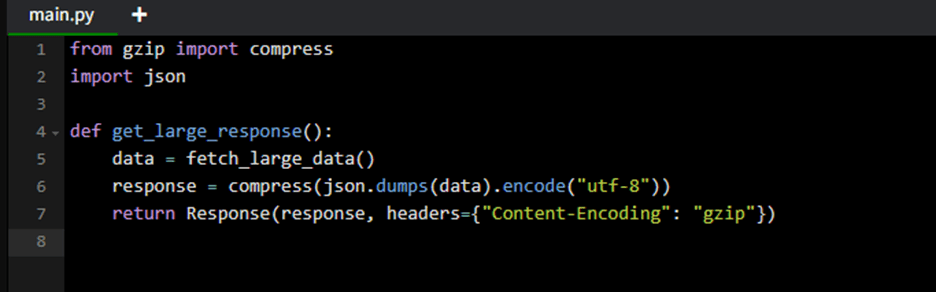
- Compress JSON responses (GZIP, Brotli).
Snippet (in prose):
Think of your API like a conversation. The smaller talk, the faster you get to the point.
Trim extra fields, and paginate results so clients never download more than they need.
Example: Select only needed fields
Example: Paginate responses
2. Caching
Key Idea: Cache smartly at multiple layers client, CDN, or backend.
Types of caching to highlight:
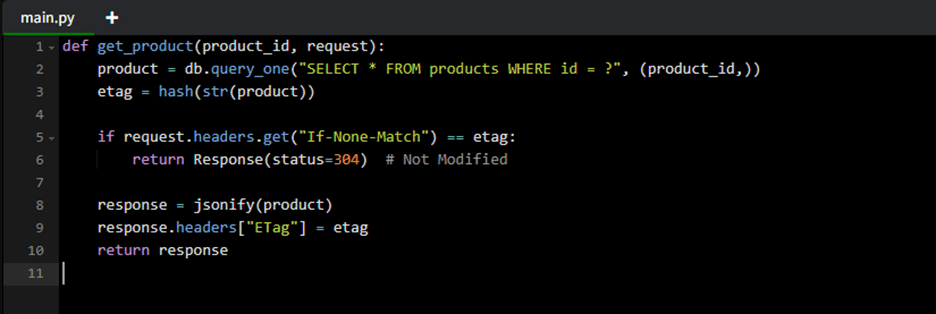
- Client-side caching using ETags or Last-Modified headers.
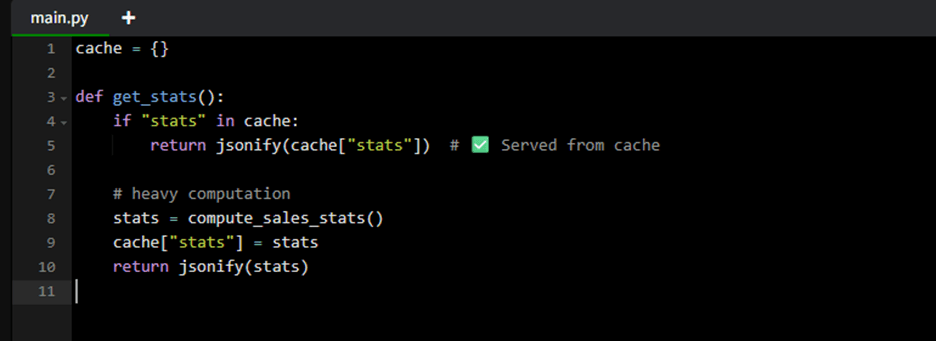
- Server-side caching of database queries or computed responses.
- Distributed caching (like Redis or Memcached).
Pro Tip:
- If your data doesn’t change frequently, a short-lived cache can save your server from redundant requests and reduce response times drastically.
Example: Client-side caching with ETag
Example: Server-side caching
3. Use Efficient Database Queries
Key Idea: APIs are only as fast as the slowest query.
Practical tips:
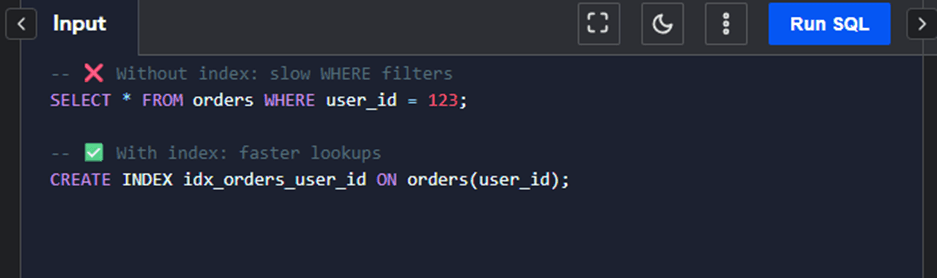
- Use indexes effectively.
- Avoid N+1 query problems.
- Pre-fetch or batch data when possible.
Tip:
Optimize your queries before scaling your infrastructure.
Example: Avoid N+1 problem
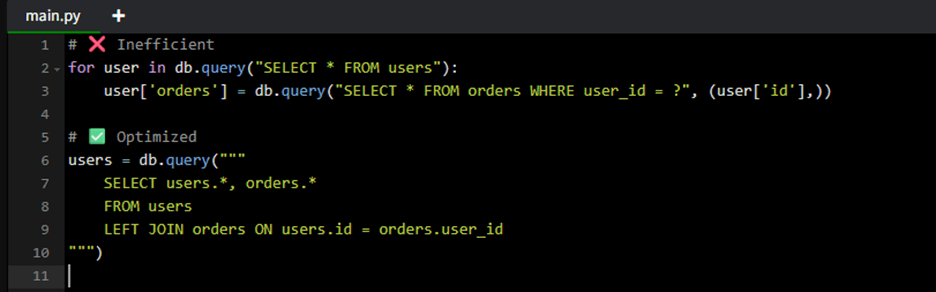
Example: Index your columns
4. Minimize Network Latency
Key Idea: Distance and hops matter — reduce both.
Tips:
- Use a CDN or edge server for static responses.
- Keep APIs close to your users (geo-distribution).
- Prefer HTTP/2 or gRPC where suitable
Example: Response compression
5. Use Asynchronous and Parallel Processing
Key Idea: Don’t block what can run in the background.
Tips:
- Queue heavy tasks (email sending, image processing).
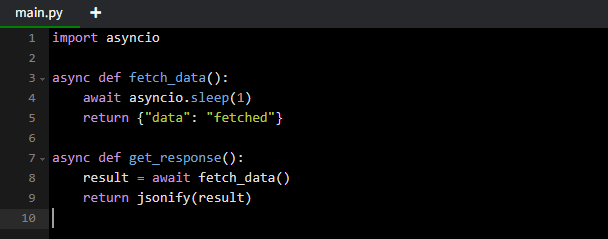
- Use async I/O for non-blocking operations.
- Split complex APIs into smaller micro-tasks.
Pro tip:
APIs feel fast not because they finish everything instantly, but because they handle time-consuming work smartly.
Example: Async I/O for faster handling
Example: Background processing (pseudo)
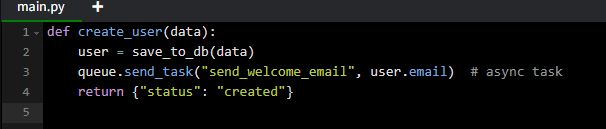
6. Monitor, Measure, and Iterate
Key Idea: You can’t improve what you don’t measure.
Metrics to track:
- Response time (P50, P90, P99)
- Error rates
- Throughput (requests per second)
Tools:
Postman Monitor, New Relic, Datadog, Signoz (open source), Prometheus + Grafana.
Tip:
Treat monitoring as part of your API design, not an afterthought. Real-world traffic always tells the truth.
Conclusion:
API optimization isn’t about one big fix it’s a series of small, measurable improvements.
Start with metrics, make a change, measure again, and repeat.
Each millisecond you shave off improves not just performance, but user satisfaction and scalability.
FAQ:
1. What are the most effective ways to improve API performance?
You can boost API performance by implementing caching, reducing payload size, optimizing database queries, enabling compression, using a CDN, and scaling your infrastructure with load balancers or microservices.
2. How does caching help in API optimization?
Caching stores frequently requested data so the server doesn’t need to process the same request repeatedly. This reduces response time, lowers server load, and improves user experience.
3. What tools can I use to monitor API performance?
Popular tools include Postman, New Relic, Datadog, Prometheus, API Gateway analytics, and Google Cloud Monitoring. These help track latency, errors, throughput, and bottlenecks.
4. Does using a CDN improve API performance?
Yes. A Content Delivery Network reduces latency by delivering responses from locations closest to users, improving speed and reducing the load on your main server.











